polarimeter principle wikipedia|polarimeter picture : fabrication Polarimetry is the measurement and interpretation of the polarization of transverse waves, most notably electromagnetic waves, such as radio or light waves. Typically polarimetry is done on electromagnetic waves that have traveled through or have been reflected, refracted or diffracted by some material in order to characterize that object. Resultado da login. TeachingBeginners. RechargePurchase. Exchange. member. Leaderboard. CustomerService. game. Click me to download.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da GayMaleTube tem os pornôs gay mais quentes. Atendemos todas as suas necessidades, fique duro como pedra em segundos. Entre e mate sua .
Polarimetry is the measurement and interpretation of the polarization of transverse waves, most notably electromagnetic waves, such as radio or light waves. Typically polarimetry is done on electromagnetic waves that have traveled through or have been reflected, refracted or diffracted by some material in order to characterize that object.
Optical rotation, also known as polarization rotation or circular birefringence, is the rotation of the orientation of the plane of polarization about the optical axis of linearly polarized light as it .A polarimeter is an instrument which measures the angle of rotation by passing polarized light through an optically active (chiral) substance. To measure optical rotation, a Light Emitting Diode (LED) produces a beam of ordinary light.
A polarimeter is an optical instrument with which one can accurately measure the angle by which the polarization of light is rotated e.g. when it passes through an optically active medium (containing chiral molecules).
A polarimeter is an instrument used to determine the angle through which plane-polarized light has been rotated by a given sample. You will have the opportunity to use a polarimeter in the . 8.2.4.1.3: Polarimetry. Page ID. Chris Schaller. College of Saint Benedict/Saint John's University. In measuring optical rotation, plane-polarized light travels down a long tube .Simply explained, polarimetry is a method of measuring the rotation of the plane of vibration of polarized light as it passes through an optically active substance. The plane of vibration of light is the direction in which the electromagnetic .Polarimetry, in analytic chemistry, measurement of the angle of rotation of the plane of polarized light (that is, a beam of light in which the vibrations of the electromagnetic waves are confined .
Polarimetry, a technique to measure the polarisation of light, is a powerful tool that allows astronomers to infer information about celestial objects, from passing comets to distant .Turn on the polarimeter and allow it to warm up for 30 minutes. Fill the polarimeter cell with a solvent that has a known specific rotation value. Place the cell in the polarimeter and adjust the polarimeter until the reading matches .
Kmitanie elektromagnetického poľa lúča obyčajného svetla prebieha neusporiadane vo všetkých rovinách kolmých na jeho smer (a). Ak vplyvom určitého prostredia prebieha kmitanie len v jednej konštantnej rovine, tzv. kmitovej rovine, hovoríme polarizovanom svetle (b).Polarimeter je vedecký prístroj, ktorým sa meria polarizácia.j
why polarimeter is used
schematic diagram of polarimeter
scratch gumball test
In measuring optical rotation, plane-polarized light travels down a long tube containing the sample. If it is a liquid, the sample may be placed in the tube as a pure liquid (its is sometimes called .En polarimeter är ett optiskt instrument som används för att mäta vridningen av polarisationsplanet hos ljus. [1] När planpolariserat ljus passerar genom vissa organiska vätskor eller lösningar av fasta ämnen, förändras ljusets svängningsriktning. Storleken på denna vridning bestäms av ämnets natur, koncentration och .Scanning laser polarimetry is the use of polarised light to measure the thickness of the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) as part of a glaucoma workup. The GDx-VCC is one example. However a Dutch study found that while there is a correlation between standard automated perimetry and GDx VCC measurements in patients with glaucoma, suggesting that GDx VCC measurements .
Heyrovský's Polarograph. Polarography is an electrochemical voltammetric technique that employs (dropping or static) mercury drop as a working electrode. In its most simple form polarography can be used to determine concentrations of electroactive species in liquids by measuring their mass-transport limiting currents.In such an experiment the potential of the .English: principle of Laurent's half-shade polarimeter. Datum: 19 Desember 2023: Bron: Eie werk: Outeur: Jcwf: Lisensiëring. Ek, die outeursreghouer van hierdie werk, publiseer dit onder die volgende lisensie: This file is made available under the Creative Commons CC0 1.0 Universal Public Domain Dedication.Principle of the polarimeter: The basic operating principle of a polarimeter includes a source that produces light with a specifically prepared linear polarization state, usually by passing through a polarizer. The light is transmitted by an optically active sample which often rotates the direction of polarization. After passing through the .
In a polarimeter (figure 2), plane-polarized light is introduced to a tube (typically 10 cm in length, figure 3) containing a solution with the substance to be measured. If the substance is optical inactive, the plane of the polarized light will not change in orientation and the observer will read an angle of [α]= 0 o. If the compound in the .A polarimeter refers to an optical instrument used to determine the polarization properties of light beams and samples. It consists of a polarization generator and analyzer, which produce and analyze a beam of known polarization state. . followed by a hybrid coupler and then the detectors. Although more complicated in principle, such a .
A polarimeter is used to measure the optical activity of a substance and consists of at least the following parts: light source; sample tube; polarization filter (analyzer) . In addition, these principles guarantee short measuring times and no mechanical wear. This ensures maximum sensitivity and the fastest compensation time over the entire .
Pyrometers principle: temperature dependence of spectral intensity of light (Planck's law), i.e. the color of the light relates to the temperature of its source, range: from about −50 °C to +4000 °C, note: measurement of thermal radiation (instead of thermal conduction, or thermal convection) means: no physical contact becomes necessary in .The polarimeter rotates the first polarizer until the photo receiver measures a transmission minimum. If the sample is optically inactive, polarizer and analyzer are now oriented perpendicular to another. . To learn more about the measuring principle of polarimetry, watch the following video: Measuring range. The measuring range of MCP .Two enantiomers of a generic amino acid that are chiral (S)-Alanine (left) and (R)-alanine (right) in zwitterionic form at neutral pH. In chemistry, a molecule or ion is called chiral (/ ˈ k aɪ r əl /) if it cannot be superposed on its mirror image by any combination of rotations, translations, and some conformational changes. This geometric property is called chirality (/ k aɪ ˈ r æ l .
English: Schematic of a polarimeter showing the principles behind its operation. Unpolarised light is passed through a polarising filter before travelling through a sample. The degree of rotation of polarisation is determined by a second, rotatable filter.In particle physics, spin polarization is the degree to which the spin, i.e., the intrinsic angular momentum of elementary particles, is aligned with a given direction. [1] This property may pertain to the spin, hence to the magnetic moment, of conduction electrons in ferromagnetic metals, such as iron, giving rise to spin-polarized currents.It may refer to (static) spin waves, preferential .The polarimeter rotates the first polarizer until the photo receiver measures a transmission minimum. If the sample is optically inactive, polarizer and analyzer are now oriented perpendicular to another. . To learn more about the .Heiland Densitometer TRDZ 1. A densitometer is a device that measures the degree of darkness (the optical density) of a photographic or semitransparent material or of a reflecting surface. [1] The densitometer is basically a light source aimed at a photoelectric cell. [2] It determines the density of a sample placed between the light source and the photoelectric cell .
To learn more about the measuring principle of refractometers, watch this video: Figure 7: Schematic setup of a refractometer. Sample to be measured is in direct contact with the measuring prism (Figure 7). The incoming light of angles less than the critical angle of total reflection is partly refracted through the sample, while incoming light .
A saccharimeter is an instrument for measuring the concentration of sugar solutions.. This is commonly achieved using a measurement of refractive index (refractometer) or the angle of rotation of polarization of optically active sugars (polarimeter).. Saccharimeters are used in food processing industries, brewing, and the distilled alcoholic drinks industry. An easily constructed and inexpensive polarimeter with an optical rotation angle resolution of about 0.5° is presented. It is made from small pieces of polarizing film, 2 LEDs, a protractor, and a few wires, all held in place with plastic interlocking toy bricks, such as Lego bricks. The instrument was used to demonstrate the optical rotation of plane polarized light as .
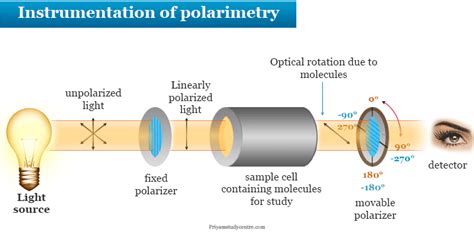
Polarimeter Figure 1 shows a principle of a polarimeter set up and its main components together with their function. Unpolarized light from the light source is first polarized. This polarized light passes through a sample cell. If an optical active substance is in a sample tube, the plane of the polarized light waves is rotated. ThePolarimeter digital otomatis. Polarimeter [1] adalah sebuah instrumen ilmiah yang digunakan untuk mengukur sudut rotasi yang disebabkan oleh lewat cahaya terpolarisasi melalui substansi optik aktif. [2]Beberapa zat kimia yang bersifat optik aktif dan terpolarisasi (uni-directional), cahaya akan berputar ke kiri (berlawanan arah jarum jam) atau kanan (searah jarum jam) .
Fig. 12.1: Schematic Diagram of Polarimeter representing its components 12.2 Principle Polarimetry is based on the fact that when a polarized light passes through the sample tube containing optically active substance it exhibits angular rotation to the left (-) or right (+). Measurement of this rotation gives the optical rotation of the substance.
Principles of Polarimetry A polarimeter consists of a polarized light source, an analyzer, a graduated circle to measure the rotation angle, and sample tubes. The polarized light passes through the sample tube and exhibits angular rotation to the left (-) or right (+). Polarimeter is the instrument used to determine the specific rotation of a compound. It consists of the following: monochromatic light source; polarizer, a prism that converts regular light into plane-polarized light; sample tube; analyzer, a prism through which the light leaving the sample is observed; see also optical rotationPolarimeter works on the principle of which of the following? change of angle of refraction with compesition. change of the electrical conductivity of sehteon with composition. pellaticntion of lithtit. Here’s the best way to solve it. Solution. Let's examine each option: 1. .
scratch garcello test
polarimeter principle pdf
webNapoleon Games Support (Frequently Asked Questions) Hulp nodig? Krijg snel antwoord op al je vragen op deze support-pagina! Ontdek de veelgestelde vragen (FAQ’s) met .
polarimeter principle wikipedia|polarimeter picture